|

|
|
|
What a coincidence... we go to
press with our Story #2 on a superconductive copper oxide tape
breakthrough by Eurotapes, who have produced 600 meters of the
tape at the Institute of Materials Science in Barcelona, thus
promising to make superconductive electricity more affordable, as
reported by Phys.org and
other news sources. At the same time, our Maryland Department of
Transportation just announced the new Baltimore-Washington
Superconducting MAGLEV
Project promising up to 300 mph
transportation with liquid helium-cooled coils levitating
the train, hosting Open House meetings in several DC area sites
in April.
In other transportation news,
our Story #1 is a revealing look at the mysterious X-37B robotic
spaceplane also called the OTV, developed years ago by the Air
Force and setting records for the longest time in orbit before it
comes back to earth. It appears that the public may be able
to see the spaceplane if it lands at Cape Canaveral.
As lithium-ion batteries seem
to be reaching their limit for energy storage, their co-inventor
just announced in Story #3 a new lithium-glass battery technology
developed at the University of Texas at Austin. Since the
alkali-doped glass electrolyte possesses a much higher dielectric
constant, it promises a much higher energy density and more
safety than lithium-ion. The
research paper is entitled, "Alternative
strategy for a safe rechargeable battery" and a patent
application has been
filed.
In the Bioenergetics realm,
Pulsed ElectroMagnetic Fields or PEMFs are an emerging trend as
the hottest electrotherapy available today at consumer prices
(see www.BioenergyDevice.org for
more info). In a recent study reported in Story #4, sponsored by
the Orthofix company, it was found that "PEMF Reduces
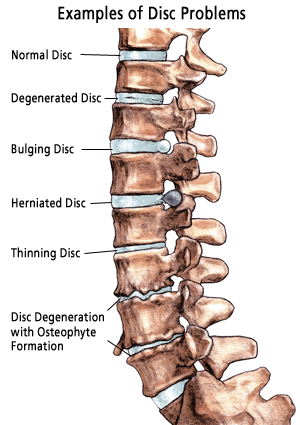
Gene Expression of Disc Degeneration" which is good news for
many people who have back problems due to intervertebral disc
issues and wish to reduce their disc degeneration.
While we have reported on the
use of waste heat to generate electricity back on May 2014
and October 2014 (See our Future
Energy eNews Archive, our Story #5 reports that a new company
in Ireland named Exergyn wants to capture the waste heat in hot
water from industrial operations, which is more energy than Saudi
Arabia's output of oil and gas. The beauty of their innovation is
to use "nitinol" which changes shape with temperature,
so it can be used as a motor prime mover.
Along the strong European trend
in renewable energy, our Story #6 emphasizes that Denmark
recently ran the country of 10 million homes on 100% renewable
energy (between onshore and offshore wind energy) for a full day.
This is a huge accomplishment, one that the US probably will have
to wait even longer for, if the Trump Administration continues
its trend to purchase and consume dirty fossil fuel that pollutes
the atmosphere with CO2, NO2, and SO2 to name a few combustion
exhaust gasses. The article also notes that Scotland, Germany,
Portugal, and Costa Rica are also some of the most impressive
countries to look at in terms of renewable energy, with Costa
Rica reaching 99% of its energy needs in 2015 with renewables
|
|
|
Our Best Selling nano
second PEMFdevice
|
|
|
Our most
popular HIgh voltage device
|
|
|
|
Best NanoSecond PEMF for
arthritis, bone issues
|
|
|
|
|
1) Air Force's X-37B Space Plane
|
|
By Mike Watt, Space.com
March 2017
The U.S. Air Force's X-37B space plane is
just eight days away from setting a record on its current
clandestine mission.
If the robotic vehicle stays aloft until March 25, it
will break the X-37B mission-duration mark of 674 days, which
was established back in October 2014. It's unclear
whether that will actually happen, however; the Air Force is
tight-lipped about most X-37B payloads and activities, including
touchdown plans
"The
landing date will be determined based on the completion of the program's
on-orbit demonstrations and objectives for this mission,"
Capt. AnnMarie Annicelli, an Air Force spokeswoman, told Space.com
via email when asked when the current mission might end.
The uncrewed X-37B (also known as the Orbital Test
Vehicle, or OTV) looks a lot like NASA's now-retired space
shuttle, only much smaller. The X-37B is just 29 feet (8.8 meters)
long and 9.6 feet (2.9 m) tall, with a wingspan of about 15 feet
(4.6 m). Two of the vehicles could fit inside a space shuttle's
payload bay.
The Air Force is known to have two X-37Bs, both of
which were built by Boeing. These twin craft have flown four
missions to date. OTV-1 launched on April 22, 2010, and landed on
Dec. 3 of that year, spending 224 days in orbit. OTV-2 started on
March 5, 2011, and wrapped up on June 16, 2012, after 468 days in
space. OTV-3 launched on Dec. 11, 2012, and landed on Oct. 17,
2014, after circling the Earth for more than 674 days. The
current mission, OTV-4, lifted off on May 20, 2015.
All four X-37B flights have launched from Florida's
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, and the first three landed at
Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. But the Air Force has
been working to consolidate X-37B launch and landing activities on
Florida's Space Coast, and that vision includes bringing the
vehicles down at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy
Space Center (KSC), which is next door to Cape Canaveral.
Rumors have swirled that OTV-4 will land at KSC, but
that's all they are at the moment - rumors. Capt. Annicelli
declined to confirm or refute such speculation. "While
the program has the capability to land at either KSC or
Vandenberg, the landing location is determined by a variety of
factors," she said.
Because of the secrecy surrounding the X-37B program,
some people have speculated that the vehicle is a space weapon.
But the Air Force has always vigorously contested such claims,
saying that the space plane is simply testing technologies and
helping researchers conduct in-space experiments.
"Technologies being tested in the program
include advanced guidance, navigation and control,
thermal-protection systems, avionics, high-temperature structures
and seals, conformal reusable insulation, lightweight
electromechanical flight systems, advanced propulsion systems and
autonomous orbital flight, re-entry, and landing," the Air
Force's
X-37B fact sheet states.
|
|
2) Superconductivity Power Breakthrough in Europe
|
|
By Tibi Puiu ZME Science March
2017
Researchers working at
the Eurotapes project, the biggest effort ever
launched by the European Commission for the development of
superconductor materials, just announced a huge breakthrough.
Namely, the researchers devised a superconductive tape that's
cheaper and more efficient than previous renditions. Such a
material is expected to form the backbone of Europe's new
electrical highways.
Don't resist progress.
Superconductivity was first discovered by Dutch
Physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes in 1911, when he and his
students found that the electrical resistance of a mercury
wire cooled to about 3.6 degrees above absolute zero made a
dramatic plunge. The drop was enormous - the resistance
became at least twenty thousand times smaller. Since then, much
work was made to improve our understanding of this peculiar state.
We now know superconductivity is a quantum mechanical phenomenon
characterized by the Meissner effect - the complete
ejection of magnetic field lines from the interior of the
superconductor as it transitions into the superconducting state.
The same effect is what causes quantum levitation.
Electricity travels on long-distance, high-voltage
transmission lines, often miles and miles across the country.
To keep losses to a minimum, the voltage in these lines can be
hundreds of thousands of volts. However, energy is still lost
because the conductor, typically made of copper, heats up. The
longer the line, the greater the losses. In fact, you can ever
hear these losses down power lines - it's that crackling sound.
Superconductivity promises to do away with such
losses - the only problem is you have to cool the superconductive
cables with liquid nitrogen. Imagine doing that for hundreds of
thousands of miles of transmission lines; it would be practically
impossible at such a large scale, which is many scientists dream
of a material that's superconductive at room temperature. Right
now, the record is held by cuprates, which have demonstrated
superconductivity at atmospheric pressure at temperatures as high
as 138 K (−135 °C), and 164 K (−109 °C) under
high pressure.
|
|
3) New Glass Battery Will Accelarate the End of Oil?
|
|
By Mark Anderson
IEEE Spectrum March 2017
John Goodenough, coinventor of the lithium-ion
battery, heads a team of researchers developing the technology
that could one day supplant it.
Electric car purchases have been on the rise lately,
posting an estimated 60 percent growth rate last year. They're
poised for rapid adoption by 2022, when EVs are
projected to cost the same as internal combustion cars. However,
these estimates all presume the incumbent lithium-ion battery
remains the go-to EV power source. So, when researchers this week
at the University of Texas at Austin unveiled a new, promising
lithium- or sodium-glass battery technology, it threatened to
accelerate even rosy projections for battery-powered cars.
"I think we have the possibility of doing what
we've been trying to do for the last 20 years," says John
Goodenough, coinventor of the now ubiquitous lithium-ion battery
and emeritus professor at the Cockrell School of Engineering at
the University of Texas, Austin. "That is, to get an electric
car that will be competitive in cost and convenience with the
internal combustion engine." Goodenough added that this new
battery technology could also store intermittent solar and wind
power on the electric grid.
Goodenough himself says that when he first coinvented
the lithium-ion battery in the 1980s, almost no one in the battery
or consumer electronics industries took the innovation seriously.
It was only Japanese labs and companies like Sony that first began
to explore the world we all today inhabit-with lithium-ions
powering nearly every portable device in the marketplace, as well
as electric vehicles and even next-generation airliners.
|
|
4) PEMF Reduces Gene Expression of Disc
Degeneration
|
|
The Spine Journal, June
2016, Volume 16, Issue 6, Pages 770-776
Ed. Note: This
is a recent, breakthrough, scholarly article which demonstrates
the efficacy of PEMF for reducing spinal disc degeneration. IRI is
proud to support such research results with its experimentally
proven www.OsteoPad.org, also shown
to increase bone density with before and after tests, in about a
six month period. With 50% of older Americans affected to some
degree with disc or bone degeneration, electrotherapy is a very
promising avenue to choose.
LEWISVILLE, Texas--(BUSINESS WIRE)-- Orthofix
International N.V. (NASDAQ:OFIX), a diversified, global medical
device company, today announced results of a cellular study
designed to determine how pulsed electromagnetic field (PEMF)
therapy affects gene expression of intervertebral discs (IVD)
cells in normal and inflammatory environments.
Published online in TheSpine
Journal, results indicate PEMF therapy may reduce cellular
inflammation and degradation associated with disc degeneration in
human IVD cells.
"The results of this study are clinically
important as they demonstrate PEMF has disease modifying
activities that may, in the future, provide a minimally-invasive
solution for patients living with painful degenerative disc
disease," said Dr. Jeffrey C. Lotz, Ph.D., Professor and Vice
Chair of Research, at the UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
and co-author of the journal article. "While an important
first step, more studies are needed to determine if this is indeed
a viable option for managing inflammation and impaired healing
associated with painful intervertebral discs."
In an in-vitro human cell culture and microarray
gene expression study, cells were stimulated to elicit the
inflammatory environment associated with degenerative disc disease
(DDD). The cells were exposed to the Orthofix
Physio-Stim® PEMF for four hours daily. At day four, this
study revealed that cells treated with PEMF showed a reduction in
proinflammatory markers and a decrease in degeneration of the
cellular matrix relative to the control group, although this
reduction did not persist to day seven.
"We continue to support preclinical evaluation
of PEMF technology to confirm and validate the potential for new
clinical applications," said Orthofix Chief Scientific
Officer and co-author James Ryaby, Ph.D. "We remain committed
to furthering the body of clinical evidence that drives best
medical practice and improved patient outcomes. We believe this
study suggests that PEMF may be an important future treatment
option for patients suffering from degenerative disc
disease."
Intervertebral disc degeneration is one of the most
common mechanical causes of chronic low back pain. It occurs when
the usually rubbery discs lose integrity as a normal process of
aging. In 2010, low back pain was ranked as the third most
burdensome condition in terms of mortality or poor health in the
U.S. by the National
Institutes for Health.
Conclusions
These results demonstrate that IVD cells are
responsive to PEMF and motivate future studies to determine
whether PEMF may be helpful for patients with IVD degeneration.
|
|
5) Turning Waste Heat into Electricity
|
|
By James Randerson,
New Scientist March 2017
A new engine that generates electricity from waste
hot water could reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions for
thousands of different businesses, from cargo shipping to data
centres.
So says Exergyn, a firm based in Dublin,
Ireland, which plans to run the first industrial trials of its
technology next year.
Globally, Exergyn estimates that the heat lost in
waste hot water from industrial processes amounts to around twice
the energy in Saudi Arabia's annual oil and gas output.
"There's just so much waste hot water in the
world," says Exergyn CEO Alan Healy. "In most cases
[companies] are actually spending energy to cool it."
Cut carbon
emissions
Cargo ships, for example, typically pump waste hot
water from the engine around the vessel to cool it down. And in data
centres, electricity-hungry fans are used to dissipate the heat
generated by rows of servers. Finding an efficient way to capture
and use this wasted energy would both reduce costs and cut carbon
emissions.
It also has another unusual quality. Unlike most
materials, nitinol expands when cooled, rather like water does
when it turns to ice (think of the mess in your freezer when you
leave a bottle of beer to cool in there too
long). "There aren't many materials in the universe that
do that," says Mike Langan, Exergyn's head of product
management.
|
|
6) Denmark Ran the Country on 100% Wind Energy
|
|
By Patrick Caughill, Futurism
News March 2017
SCANDINAVIAN SUSTAINABILITY
Countries all over the world are making major strides
in renewable energy. Many nations are investing in new clean
energy infrastructure that is allowing them to supply enough power
to meet their energy needs by great percentages, if not entirely.
On February 22nd, Denmark generated enough energy
with its wind turbines to power the entire country for the day. An
especially windy day allowed the turbines to generate 97
gigawatt-hours (GWh) of energy. 70 of those GWh came from onshore
wind turbines and the remaining 27 GWh from offshore
installations. All of this power, generated from a single type of
renewable energy, is enough to power 10 million average EU homes.
This boost in wind power generation is partly thanks
to a new offshore wind turbine installation that was able to break
the record for the most energy generated by a single turbine
in a 24-hour period. Many European countries have been
sharing similar accomplishments. Wind Europe spokesman Oliver
Joy said, "In 2016 we saw the UK was powered without
coal for 12 and a half hours, Germany went some days on renewable,
and Portugal went four straight days on renewable. It shows
energy transition is underway in Europe and arguably further ahead
than anywhere else in the world."
Scotland has also been investing heavily in renewable
energy with wind turbines that could power every
household for an entire month. Last year, the country also
launched the world's first large-scale tidal power
farm that has to potential to power 175,000 homes.
Costa Rica is one of the most impressive countries to
look at in terms of renewable energy. It's is able to run entirely
on renewable energy for months at a time. In fact, in 2015
the country met 99 percent of its total energy need from
renewable sources alone.
|
|
If you enjoy this
service, please consider making a donation by clicking on
the button below. We are a 501 (C)3 Non Profit Institute and your
donations are fully deductible to the maximum allowed by law.
We are registered with the Non-Profit directory GUIDESTAR
and have a GoldStar Rating.
|
|
|
Shopping at Amazon? click here
& 0.5% will be donated to IRI
|
|
|
|
|
|

|
![]()